ANSI compliance in Databricks Runtime
Applies to: ![]() Databricks Runtime
Databricks Runtime
This article describes ANSI compliance in Databricks Runtime. For ANSI mode in Databricks SQL, see ANSI_MODE.
Spark SQL has two options to support compliance with the ANSI SQL standard: spark.sql.ansi.enabled and spark.sql.storeAssignmentPolicy.
When spark.sql.ansi.enabled is set to true, Spark SQL uses an ANSI compliant dialect instead of being Hive compliant. For example, Spark will throw an exception at runtime instead of returning null results if the inputs to a SQL operator/function are invalid. Some ANSI dialect features may be not from the ANSI SQL standard directly, but their behaviors align with ANSI SQL’s style.
Moreover, Spark SQL has an independent option to control implicit casting behaviors when storing rows in a table. The casting behaviors are defined as store assignment rules in the standard.
When spark.sql.storeAssignmentPolicy is set to ANSI, Spark SQL complies with the ANSI store assignment rules. This is a separate configuration because its default value is ANSI, while the configuration spark.sql.ansi.enabled is disabled by default.
The following table summarizes the behavior:
| Property Name | Default | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
spark.sql.ansi.enabled | false | When true, Spark attempts to conform to the ANSI SQL specification: - Throws a runtime exception if an overflow occurs in any operation on an integer or decimal field. - Forbids using the reserved keywords of ANSI SQL as identifiers in the SQL parser. |
spark.sql.storeAssignmentPolicy | ANSI | When storing a value into a column with a different data type, Spark performs type conversion. There are three policies for the type coercion rules: ANSI, legacy, and strict.- ANSI: Spark performs the type coercion as per ANSI SQL. In practice, the behavior is mostly the same as PostgreSQL. It disallows certain unreasonable type conversions such as converting string to int or double to boolean.- legacy: Spark allows the type coercion as long as it is a valid Cast, which is very loose. For example, converting string to int or double to boolean is allowed. It is also the only behavior in Spark 2.x and it is compatible with Hive.- strict: Spark doesn’t allow any possible precision loss or data truncation in type coercion, for example, converting double to int or decimal to double is not allowed. |
The following subsections present behavior changes in arithmetic operations, type conversions, and SQL parsing when ANSI mode is enabled. For type conversions in Spark SQL, there are three kinds of them and this article will introduce them one by one: cast, store assignment and type coercion.
Arithmetic operations
In Spark SQL, arithmetic operations performed on numeric types (with the exception of decimal) are not checked for overflows by default.
This means that in case an operation causes overflows, the result is the same with the corresponding operation in a Java or Scala program (For example, if the sum of 2 integers is higher than the maximum value representable, the result is a negative number). On the other hand, Spark SQL returns null for decimal overflows.
When spark.sql.ansi.enabled is set to true and an overflow occurs in numeric and interval arithmetic operations, it throws an arithmetic exception at runtime.
-- `spark.sql.ansi.enabled=true`
> SELECT 2147483647 + 1;
error: integer overflow
-- `spark.sql.ansi.enabled=false`
> SELECT 2147483647 + 1;
-2147483648
Cast
When spark.sql.ansi.enabled is set to true, explicit casting by CAST syntax throws a runtime exception for illegal cast patterns defined in the standard, such as casts from a string to an integer.
The CAST clause of Spark ANSI mode follows the syntax rules of section 6.13 “cast specification” in
ISO/IEC 9075-2:2011 Information technology — Database languages - SQL — Part 2: Foundation (SQL/Foundation),
except it specially allows the following straightforward type conversions which are disallowed as per the ANSI standard:
- NumericType <=> BooleanType
- StringType <=> BinaryType
The valid combinations of source and target data type in a CAST expression are given by the following table.
“Y” indicates that the combination is syntactically valid without restriction and “N” indicates that the combination is not valid.
| SourceTarget | Numeric | String | Date | Timestamp | Interval | Boolean | Binary | Array | Map | Struct |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numeric | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N |
| String | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N |
| Date | N | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| Timestamp | N | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| Interval | N | Y | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N |
| Boolean | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N |
| Binary | Y | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N |
| Array | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N |
| Map | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N |
| Struct | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y |
-- Examples of explicit casting
-- `spark.sql.ansi.enabled=true`
> SELECT CAST('a' AS INT);
ERROR: [CAST_INVALID_INPUT] The value 'a' of the type "STRING" cannot be cast to "INT" because it is malformed.
> SELECT CAST(2147483648L AS INT);
ERROR: [CAST_OVERFLOW] The value 2147483648L of the type "BIGINT" cannot be cast to "INT" due to an overflow.
> SELECT CAST(DATE'2020-01-01' AS INT)
ERROR: [DATATYPE_MISMATCH.CAST_WITH_FUNC_SUGGESTION] Cannot resolve "CAST(DATE '2020-01-01' AS INT)" due to data type mismatch: cannot cast "DATE" to "INT".
-- `spark.sql.ansi.enabled=false` (This is a default behavior)
> SELECT cast('a' AS INT);
null
> SELECT CAST(2147483648L AS INT);
-2147483648
> SELECT CAST(DATE'2020-01-01' AS INT);
null
Store assignment
The setting spark.sql.storeAssignmentPolicy defaults to ANSI. With this setting, when the data types of source values doesn’t match the target column types, Spark SQL automatically adds ANSI CAST clauses to the INSERT statement.
During table insertion under this policy, Spark checks for and rejects invalid casts, throwing an exception to ensure data quality. This means if an insertion attempt fails due to a type mismatch, it will not result in any data being partially written to the table.
Examples:
-- spark.sql.storeAssignmentPolicy=ANSI
> CREATE TABLE test(i INT);
> INSERT INTO test VALUES (2147483648L);
ERROR: [CAST_OVERFLOW_IN_TABLE_INSERT] Fail to insert a value of "BIGINT" type into the "INT" type column `i` due to an overflow.
> INSERT INTO test VALUES ('a');
ERROR: [CAST_INVALID_INPUT ERROR] The value 'a' of the type "STRING" cannot be cast to "INT" because it is malformed
These examples show Spark SQL preventing incompatible data from being inserted, thereby maintaining data integrity.
When the spark.sql.storeAssignmentPolicy is set to LEGACY, Spark SQL reverts to the behavior prevalent up to Spark 2.x. In this mode, instead of using ANSI CAST, it applies legacy CAST operations. Under this policy, invalid casts during table insertions result in either NULL values or incorrect values being inserted, rather than throwing an exception.
Examples:
-- spark.sql.storeAssignmentPolicy=LEGACY
> CREATE TABLE test(i INT);
> INSERT INTO test VALUES (2147483648L);
> INSERT INTO test VALUES ('a');
> SELECT * FROM test;
-- Results
-- -2147483648 (incorrect value due to overflow)
-- null (cannot cast 'a' to INT)
Type coercion
Type Promotion and Precedence
When spark.sql.ansi.enabled is set to true, Spark SQL uses several rules that govern how conflicts between data types are resolved.
At the heart of this conflict resolution is the Type Precedence List which defines whether values of a given data type can be promoted to another data type implicitly.
| Data type | precedence list(from narrowest to widest) |
|---|---|
| Byte | Byte -> Short -> Int -> Long -> Decimal -> Float* -> Double |
| Short | Short -> Int -> Long -> Decimal-> Float* -> Double |
| Int | Int -> Long -> Decimal -> Float* -> Double |
| Long | Long -> Decimal -> Float* -> Double |
| Decimal | Decimal -> Float* -> Double |
| Float | Float -> Double |
| Double | Double |
| Date | Date -> Timestamp |
| Timestamp | Timestamp |
| String | String |
| Binary | Binary |
| Boolean | Boolean |
| Interval | Interval |
| Map | Map** |
| Array | Array** |
| Struct | Struct** |
- For least common type resolution float is skipped to avoid loss of precision.
** For a complex type, the precedence rule applies recursively to its component elements.
Special rules apply for the String type and untyped NULL. A NULL can be promoted to any other type, while a String can be promoted to any simple data type.
This is a graphical depiction of the precedence list as a directed tree:
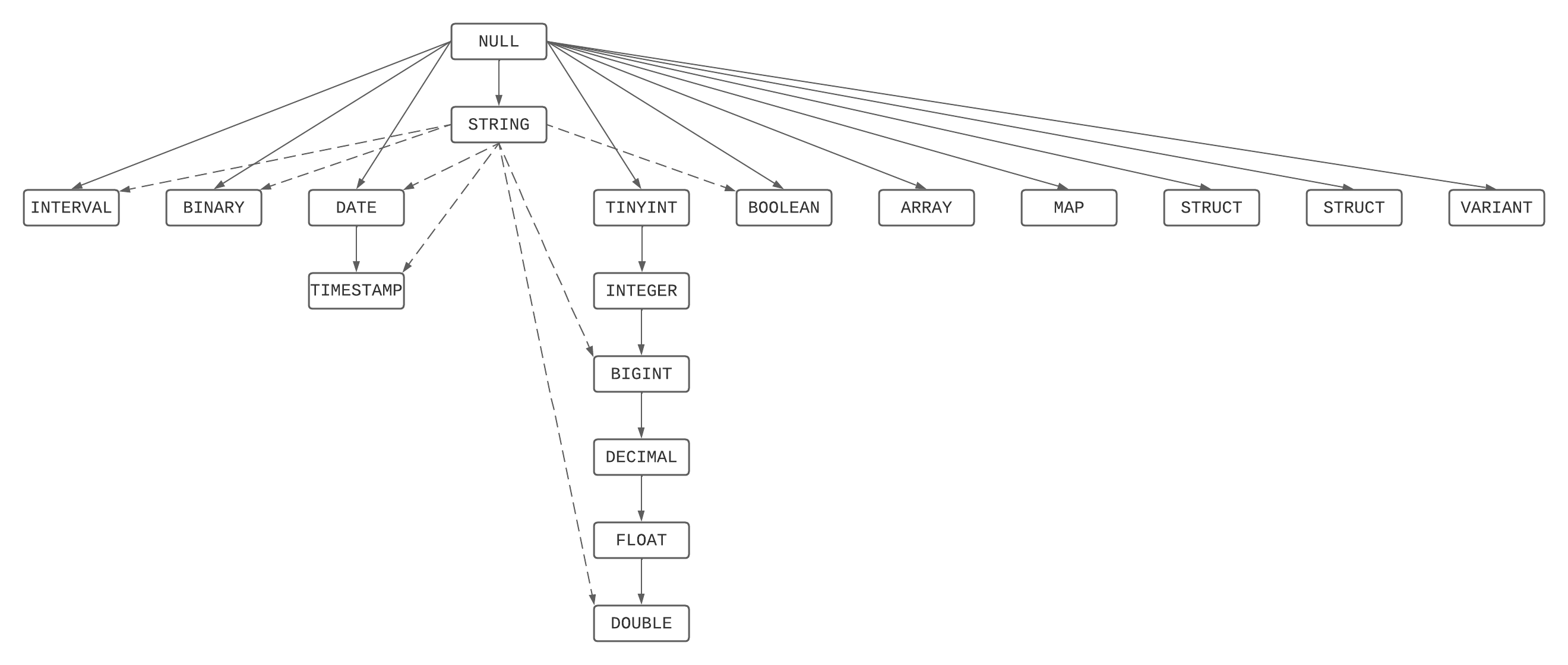
Least Common Type Resolution
The least common type from a set of types is the narrowest type reachable from the precedence list by all elements of the set of types.
The least common type resolution is used to:
- Decide whether a function expecting a parameter of a type can be invoked using an argument of a narrower type.
- Derive the argument type for functions which expect a shared argument type for multiple parameters, such as coalesce, least, or greatest.
- Derive the operand types for operators such as arithmetic operations or comparisons.
- Derive the result type for expressions such as the case expression.
- Derive the element, key, or value types for array and map constructors.
Special rules are applied if the least common type resolves to FLOAT. With float type values, if any of the types is INT, BIGINT, or DECIMAL the least common type is pushed to DOUBLE to avoid potential loss of digits.
-- The coalesce function accepts any set of argument types as long as they share a least common type.
-- The result type is the least common type of the arguments.
> SET spark.sql.ansi.enabled=true;
> SELECT typeof(coalesce(1Y, 1L, NULL));
BIGINT
> SELECT typeof(coalesce(1, DATE'2020-01-01'));
Error: Incompatible types [INT, DATE]
> SELECT typeof(coalesce(ARRAY(1Y), ARRAY(1L)));
ARRAY<BIGINT>
> SELECT typeof(coalesce(1, 1F));
DOUBLE
> SELECT typeof(coalesce(1L, 1F));
DOUBLE
> SELECT (typeof(coalesce(1BD, 1F)));
DOUBLE
-- The substring function expects arguments of type INT for the start and length parameters.
> SELECT substring('hello', 1Y, 2);
he
> SELECT substring('hello', '1', 2);
he
> SELECT substring('hello', 1L, 2);
Error: Argument 2 requires an INT type.
> SELECT substring('hello', str, 2) FROM VALUES(CAST('1' AS STRING)) AS T(str);
Error: Argument 2 requires an INT type.
SQL functions
The behavior of some SQL functions can be different under ANSI mode (spark.sql.ansi.enabled=true).
size: This function returns null for null input under ANSI mode.element_at:- This function throws
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsExceptionif using invalid indices. - This function throws
NoSuchElementExceptionif key does not exist in map.
- This function throws
elt: This function throwsArrayIndexOutOfBoundsExceptionif using invalid indices.make_date: This function fails with an exception if the result date is invalid.make_timestamp: This function fails with an exception if the result timestamp is invalid.make_interval: This function fails with an exception if the result interval is invalid.next_day: This function throwsIllegalArgumentExceptionif input is not a valid day of week.parse_url: This function throwsIllegalArgumentExceptionif an input string is not a valid url.to_date: This function fails with an exception if the input string can’t be parsed, or the pattern string is invalid.to_timestamp: This function fails with an exception if the input string can’t be parsed, or the pattern string is invalid.to_unix_timestamp: This function fails with an exception if the input string can’t be parsed, or the pattern string is invalid.unix_timestamp: This function fails with an exception if the input string can’t be parsed, or the pattern string is invalid.
SQL operators
The behavior of some SQL operators can be different under ANSI mode (spark.sql.ansi.enabled=true).
array_col[index]: This operator throwsArrayIndexOutOfBoundsExceptionif using invalid indices.map_col[key]: This operator throwsNoSuchElementExceptionif key does not exist in map.CAST(string_col AS TIMESTAMP): This operator fails with an exception if the input string can’t be parsed.CAST(string_col AS DATE): This operator fails with an exception if the input string can’t be parsed.
Useful Functions for ANSI Mode
When ANSI mode is on, it throws exceptions for invalid operations. You can use the following SQL functions to suppress such exceptions.
try_cast: identical toCAST, except that it returnsNULLresult instead of throwing an exception on runtime error.try_add: identical to the add operator+, except that it returnsNULLresult instead of throwing an exception on integral value overflow.try_divide: identical to the division operator/, except that it returnsNULLresult instead of throwing an exception on dividing 0.
SQL keywords
When spark.sql.ansi.enabled is true, Spark SQL will use the ANSI mode parser.
In this mode, Spark SQL has two kinds of keywords:
- Reserved keywords: Keywords that are reserved and can’t be used as identifiers for table, view, column, function, alias, etc.
- Non-reserved keywords: Keywords that have a special meaning only in particular contexts and can be used as identifiers in other contexts. For example,
EXPLAIN SELECT ...is a command, but EXPLAIN can be used as identifiers in other places.
When the ANSI mode is disabled, Spark SQL has two kinds of keywords:
- Non-reserved keywords: Same definition as the one when the ANSI mode enabled.
- Strict-non-reserved keywords: A strict version of non-reserved keywords, which cannot be used as table alias.
By default spark.sql.ansi.enabled is false.
Below is a list of all the keywords in Spark SQL.
| Keyword | Spark SQL ANSI Mode | Spark SQL Default Mode | SQL-2016 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADD | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| AFTER | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| ALL | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| ALTER | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| ALWAYS | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| ANALYZE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| AND | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| ANTI | non-reserved | strict-non-reserved | non-reserved |
| ANY | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| ARCHIVE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| ARRAY | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| AS | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| ASC | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| AT | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| AUTHORIZATION | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| BETWEEN | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| BOTH | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| BUCKET | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| BUCKETS | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| BY | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| CACHE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| CASCADE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| CASE | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| CAST | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| CHANGE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| CHECK | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| CLEAR | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| CLUSTER | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| CLUSTERED | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| CODEGEN | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| COLLATE | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| COLLECTION | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| COLUMN | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| COLUMNS | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| COMMENT | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| COMMIT | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| COMPACT | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| COMPACTIONS | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| COMPUTE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| CONCATENATE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| CONSTRAINT | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| COST | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| CREATE | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| CROSS | reserved | strict-non-reserved | reserved |
| CUBE | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| CURRENT | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| CURRENT_DATE | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| CURRENT_TIME | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| CURRENT_USER | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| DATA | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| DATABASE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| DATABASES | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| DAY | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| DBPROPERTIES | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| DEFINED | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| DELETE | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| DELIMITED | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| DESC | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| DESCRIBE | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| DFS | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| DIRECTORIES | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| DIRECTORY | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| DISTINCT | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| DISTRIBUTE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| DIV | non-reserved | non-reserved | not a keyword |
| DROP | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| ELSE | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| END | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| ESCAPE | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| ESCAPED | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| EXCEPT | reserved | strict-non-reserved | reserved |
| EXCHANGE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| EXISTS | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| EXPLAIN | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| EXPORT | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| EXTENDED | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| EXTERNAL | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| EXTRACT | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| FALSE | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| FETCH | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| FIELDS | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| FILTER | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| FILEFORMAT | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| FIRST | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| FN | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| FOLLOWING | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| FOR | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| FOREIGN | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| FORMAT | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| FORMATTED | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| FROM | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| FULL | reserved | strict-non-reserved | reserved |
| FUNCTION | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| FUNCTIONS | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| GENERATED | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| GLOBAL | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| GRANT | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| GRANTS | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| GROUP | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| GROUPING | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| HAVING | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| HOUR | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| IF | non-reserved | non-reserved | not a keyword |
| IGNORE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| IMPORT | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| IN | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| INDEX | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| INDEXES | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| INNER | reserved | strict-non-reserved | reserved |
| INPATH | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| INPUTFORMAT | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| INSERT | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| INTERSECT | reserved | strict-non-reserved | reserved |
| INTERVAL | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| INTO | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| IS | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| ITEMS | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| JOIN | reserved | strict-non-reserved | reserved |
| JSON | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| KEY | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| KEYS | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| LAST | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| LATERAL | reserved | strict-non-reserved | reserved |
| LAZY | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| LEADING | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| LEFT | reserved | strict-non-reserved | reserved |
| LIKE | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| ILIKE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| LIMIT | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| LINES | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| LIST | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| LOAD | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| LOCAL | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| LOCATION | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| LOCK | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| LOCKS | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| LOGICAL | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| MACRO | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| MAP | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| MATCHED | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| MERGE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| MINUTE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| MINUS | non-reserved | strict-non-reserved | non-reserved |
| MONTH | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| MSCK | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| NAMESPACE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| NAMESPACES | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| NATURAL | reserved | strict-non-reserved | reserved |
| NO | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| NOT | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| NULL | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| NULLS | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| OF | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| ON | reserved | strict-non-reserved | reserved |
| ONLY | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| OPTION | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| OPTIONS | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| OR | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| ORDER | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| OUT | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| OUTER | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| OUTPUTFORMAT | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| OVER | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| OVERLAPS | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| OVERLAY | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| OVERWRITE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| PARTITION | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| PARTITIONED | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| PARTITIONS | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| PERCENT | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| PIVOT | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| PLACING | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| POSITION | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| PRECEDING | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| PRIMARY | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| PRINCIPALS | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| PROPERTIES | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| PURGE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| QUALIFY | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| QUERY | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| RANGE | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| RECIPIENT | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| RECIPIENTS | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| RECORDREADER | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| RECORDWRITER | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| RECOVER | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| REDUCE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| REFERENCES | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| REFRESH | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| REGEXP | non-reserved | non-reserved | not a keyword |
| REMOVE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| RENAME | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| REPAIR | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| REPLACE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| RESET | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| RESPECT | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| RESTRICT | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| REVOKE | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| RIGHT | reserved | strict-non-reserved | reserved |
| RLIKE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| ROLE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| ROLES | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| ROLLBACK | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| ROLLUP | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| ROW | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| ROWS | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| SCHEMA | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| SCHEMAS | non-reserved | non-reserved | not a keyword |
| SECOND | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| SELECT | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| SEMI | non-reserved | strict-non-reserved | non-reserved |
| SEPARATED | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| SERDE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| SERDEPROPERTIES | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| SESSION_USER | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| SET | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| SETS | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| SHARE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| SHARES | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| SHOW | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| SKEWED | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| SOME | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| SORT | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| SORTED | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| START | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| STATISTICS | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| STORED | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| STRATIFY | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| STRUCT | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| SUBSTR | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| SUBSTRING | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| SYNC | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| TABLE | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| TABLES | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| TABLESAMPLE | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| TBLPROPERTIES | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| TEMP | non-reserved | non-reserved | not a keyword |
| TEMPORARY | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| TERMINATED | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| THEN | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| TIME | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| TO | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| TOUCH | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| TRAILING | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| TRANSACTION | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| TRANSACTIONS | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| TRANSFORM | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| TRIM | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| TRUE | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| TRUNCATE | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| TRY_CAST | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| TYPE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| UNARCHIVE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| UNBOUNDED | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| UNCACHE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| UNION | reserved | strict-non-reserved | reserved |
| UNIQUE | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| UNKNOWN | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| UNLOCK | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| UNSET | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| UPDATE | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| USE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| USER | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| USING | reserved | strict-non-reserved | reserved |
| VALUES | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| VIEW | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| VIEWS | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| WHEN | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| WHERE | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| WINDOW | non-reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| WITH | reserved | non-reserved | reserved |
| YEAR | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |
| ZONE | non-reserved | non-reserved | non-reserved |